An In-Depth Overview of the Philippine Healthcare System
- Introduction to the Philippine healthcare system
- What kind of healthcare system does the Philippines have?
- The public healthcare system in the Philippines
- The private healthcare system in the Philippines
- How healthcare in the Philippines is funded
- Sponsored Members
- Indigents
- Lifetime Members
- Senior Citizens
- Formal Sector Employees
- Informal Economy
- Healthcare issues in the Philippines
- “Brain Drain” phenomenon
- H3: 2. Shortcomings in addiction treatment and care
- Slow emergency response
- Reproductive care in the Philippines
- Mental health and addiction treatment
- Government initiatives to improve the Philippine healthcare system
- Increasing funding for the healthcare sector
- Implementing health insurance programs
- Improving healthcare infrastructure
- FAQs about the Philippine healthcare system
The Philippine healthcare system is a combination of public and private healthcare providers aimed at providing access to healthcare services to all Filipinos, regardless of their socio-economic status.
In this article, we will explore the current state of the Philippine healthcare system, including its strengths and weaknesses, and look at ways to improve it for the benefit of all Filipinos.
Introduction to the Philippine healthcare system
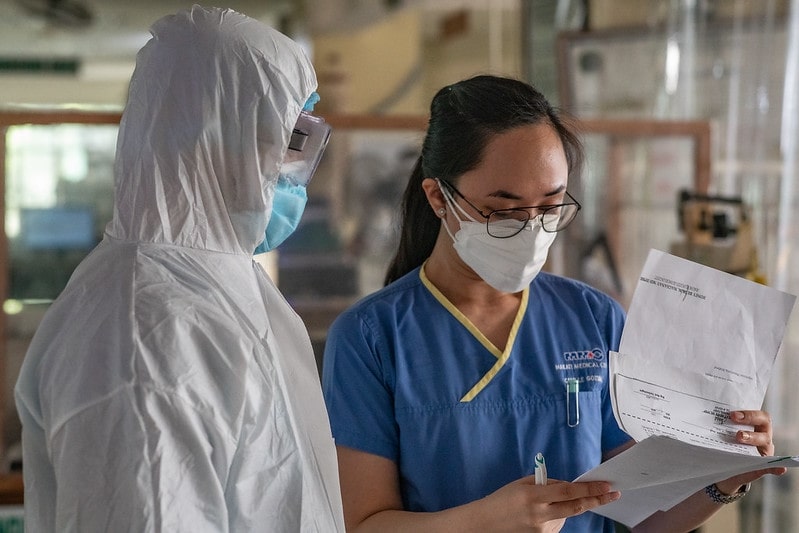

The healthcare system in the Philippines is a complex network of public and private healthcare providers, health insurance programs, and government initiatives to improve the health and well-being of Filipinos.
The public healthcare system in the Philippines has skilled hospital staff, but there are differences between healthcare in urban and rural areas.
Many Filipinos depend on public healthcare, but the high number of medical staff leaving for other countries puts the system under pressure.
This means that some hospitals are short-staffed, and patients may have to wait longer for treatment.
Philhealth, a government-run company, manages public healthcare in the Philippines. It pays for some medical treatments and costs, such as hospital stays and non-emergency procedures, but not all of them.
For people from other countries working in the Philippines, it is required to enroll in Philhealth. Employers, employees, and the government all contribute to Philhealth.
Non-citizens living in the Philippines legally can also enroll.
Even though healthcare problems exist in the Philippines, the system is improving. The government is working towards a universal healthcare system, which means that Philhealth now provides free medical treatment to all Filipino citizens.
The Universal Healthcare Act passed in 2019 also made sure that Philhealth covers consultations and lab tests. All Filipino citizens are automatically signed up for the national program.
What kind of healthcare system does the Philippines have?
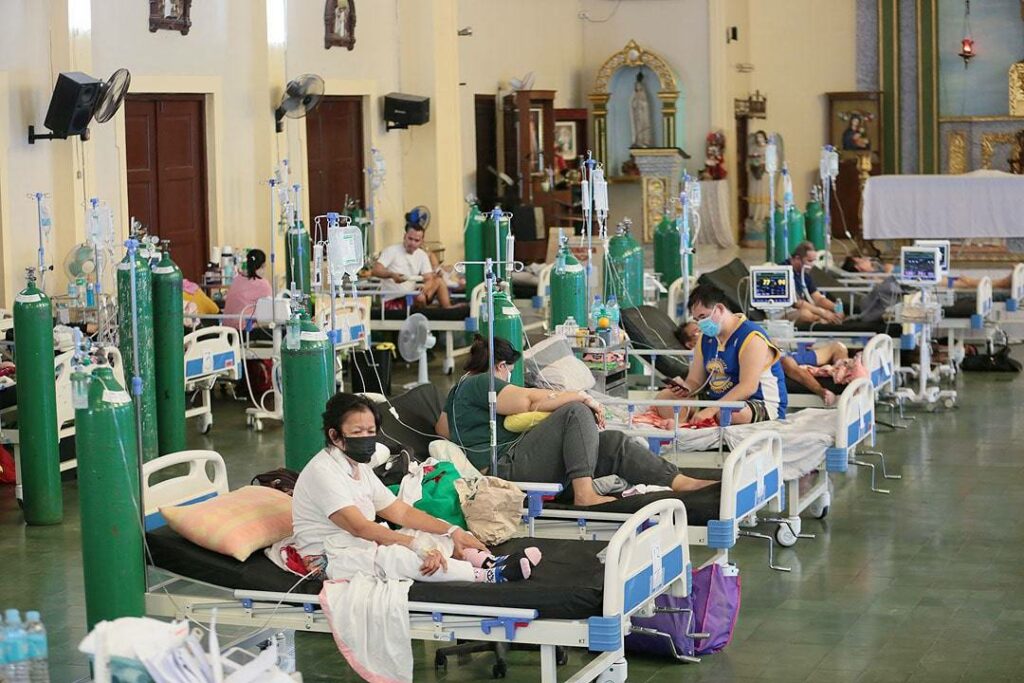
The Philippine healthcare system features a combination of public and private services.
The government provides healthcare services through public hospitals and clinics, while private healthcare providers cater to those who can afford to pay for specific medical treatments.
The system is made up of a combination of public and private healthcare providers, government-sponsored health insurance programs, and initiatives aimed at improving the health and well-being of Filipinos.
The public healthcare system in the Philippines
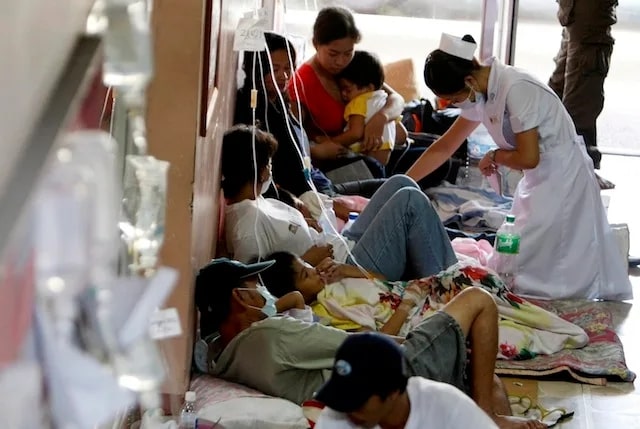

The public healthcare system in the Philippines is an indispensable part of the country’s healthcare system, serving a large part of the population.
It includes government-run hospitals, health centers, and barangay health stations that provide basic medical services.
One of the best things about the public healthcare system in the Philippines is PhilHealth, a national health insurance program.
PhilHealth helps people pay for their medical treatment and ensures everyone has access to quality healthcare, especially those from low-income families.
The public healthcare system also offers preventative services like check-ups, vaccinations, and treatment for common illnesses to help keep people healthy.
Plus, they have special services for pregnant women, new mothers, and newborns.
The private healthcare system in the Philippines
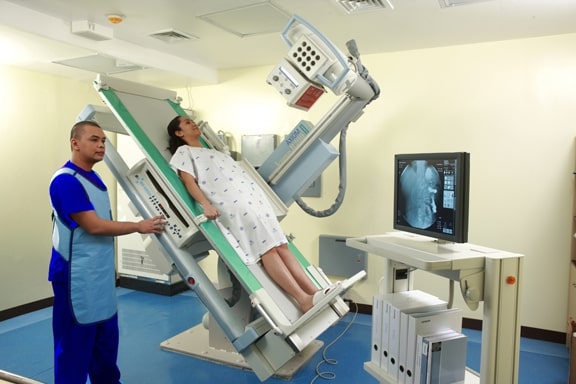
The private healthcare system in the Philippines is run by private organizations like hospitals and clinics and offers a higher level of medical care compared to the public system.
One thing that makes private healthcare so special is the wide range of services available, including specialized treatments and advanced diagnostic facilities.
This allows patients to receive more focused and specialized care for their medical conditions.
However, it comes at a higher cost. Services in the private system are more expensive, and patients often need to pay out-of-pocket or have private health insurance to cover the cost.
How healthcare in the Philippines is funded

The Philippines has a public healthcare program called PhilHealth, which was created in 1995 with the goal of making healthcare accessible and affordable for everyone.
The government, employers, and employees all contribute to funding PhilHealth. It also offers different medical plans based on factors like age, income, and health status.
Six different groups can become members of PhilHealth:
1. Sponsored Members
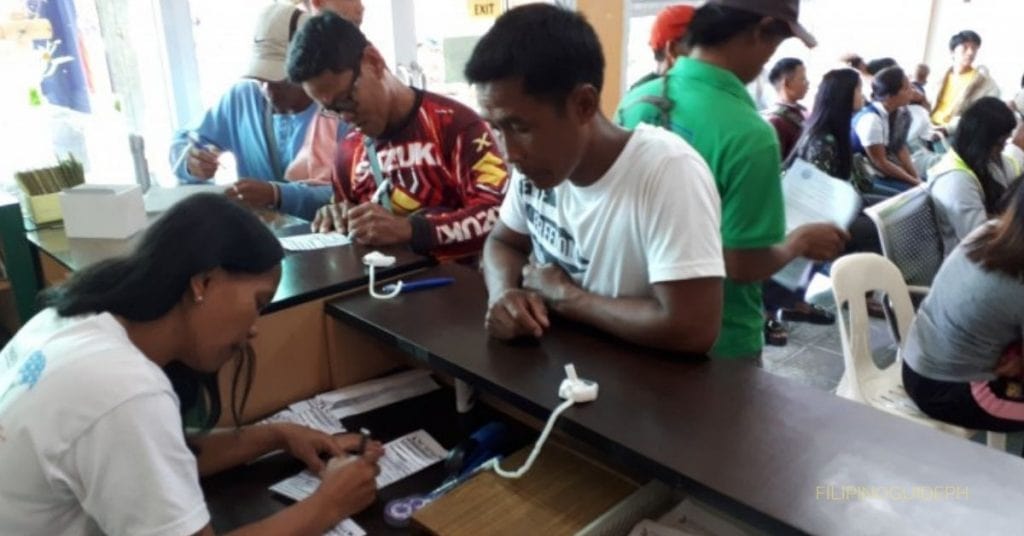

People who are eligible for PhilHealth coverage under this category are those who the local government subsidizes. This group is typically composed of those who need financial assistance to access healthcare services.
The local government provides support in the form of paying for the PhilHealth premiums of these individuals. This ensures they have access to quality healthcare services even if they do not have the means to pay for them independently.
2. Indigents
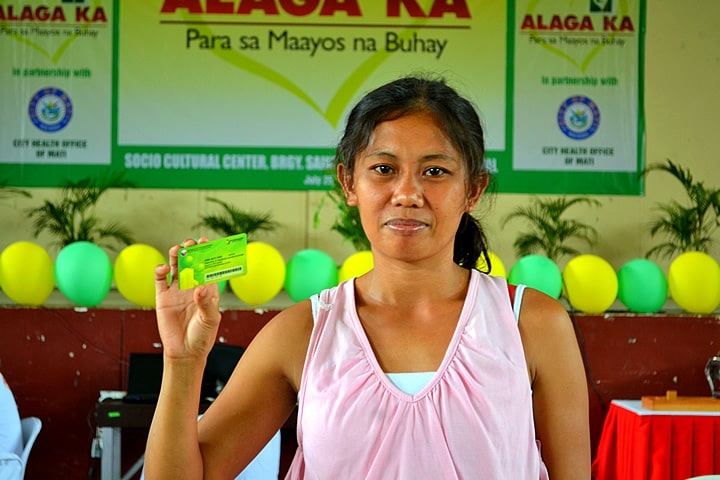

Individuals with low or no income are considered indigents and eligible for PhilHealth coverage under this category. This group is comprised of those who are struggling financially and need support in accessing healthcare services.
With PhilHealth coverage, they can receive quality medical treatment without worrying about the cost. This is a crucial aspect of the program, as it ensures that no one is left without access to healthcare simply because they cannot afford it.
3. Lifetime Members
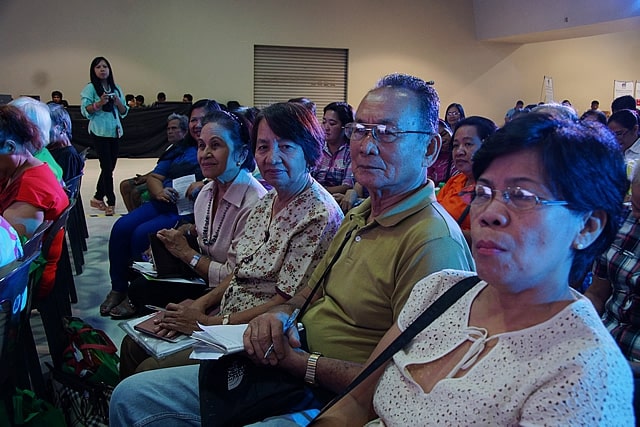

Retirees and pensioners over 60 years old who have paid their PhilHealth premiums for at least 120 months become Lifetime Members.
This category is specifically designed for individuals who have been contributing to the program for an extended period of time. As a reward, they are no longer required to pay premiums and can enjoy free PhilHealth coverage for the rest of their lives.
4. Senior Citizens

People over 60 years old and not covered by any other PhilHealth membership categories are eligible for free PhilHealth coverage as senior citizens.
This category ensures that even those who do not fall under the other categories can still access quality healthcare services. The coverage allows senior citizens to receive medical treatment without worrying about the cost.
5. Formal Sector Employees

Employees of both public and private businesses are eligible for PhilHealth coverage under this category. This group is composed of those who are working in formal sector jobs and have a steady income.
They are required to pay a portion of their salary towards their PhilHealth premiums, while their employers also contribute a share. This ensures they have access to quality healthcare services whenever needed.
6. Informal Economy

Self-employed individuals, migrant workers, and people who do not fit into the formal sector are eligible for PhilHealth coverage under this category.
This group is composed of those who work in the informal economy and may not have a steady source of income.
Contributions from the individual and the government fund the coverage for this category. This category is popular among expats residing in the Philippines, as it provides them with access to quality healthcare services while in the country.
Healthcare issues in the Philippines
The Philippines has some major problems when it comes to healthcare. Here are three of the biggest:
1. “Brain Drain” phenomenon
The Philippines is facing a serious issue called “Brain Drain.” This happens when highly skilled people, like doctors, leave the country to work elsewhere. As a result, the medical industry in the Philippines is short-staffed.
There aren’t enough doctors to take care of everyone in the country. For example, there’s only one doctor for every 33,000 people. Patients often have to wait a long time to see a doctor, and their quality of care can suffer.
Recently, the government has started giving money to medical students so they can begin their careers in the Philippines. This is an effort to keep more doctors in the country.
H3: 2. Shortcomings in addiction treatment and care

The Philippines is fighting a war on drugs, and thousands of people have been killed. People who use drugs can also be imprisoned for a long time.
Some government-run rehabilitation centers can provide a safe place for people to get help, but most centers are overcrowded.
This means that doctors are overworked and can’t give patients the one-on-one care they need. Activists say that the government is not doing enough to address the root causes of addiction, like poverty and hunger.
If someone has enough money, they may have to go to another country to get the help they need.
3. Slow emergency response

The quality of ambulance services in the Philippines varies a lot, and there aren’t enough laws to regulate them.
This means that emergency services can be slow to respond, and the care patients receive before they reach the hospital may not be good enough.
Private ambulances are better equipped and have faster response times, but they can be expensive. Some private hospitals offer ambulance services as part of a medical insurance package, and people can pay a monthly fee.
Reproductive care in the Philippines

The Philippines, which is primarily Catholic, used to have a difficult time with the legality of female hormonal contraceptives. Nowadays, birth control options have become more accessible.
Women now have access to various methods of contraception, such as long-lasting options like IUDs and subdermal implants, as well as hormonal pills and injections.
However, emergency contraception is not readily available in the country, and abortion is illegal, even in cases of rape or incest.
Terminating a pregnancy that could threaten the life of the person carrying it is also not easily accessible, and its legality is uncertain.
Mental health and addiction treatment

If you’re living in a city in the Philippines, finding help for mental health issues is easy. Hospitals offer these services, and there are also private clinics and psychiatrists to visit.
Unfortunately, getting this type of care is more difficult if you live in a rural area.
The Philippines has had a tough time with drug use. The government has tried to stop it with a “war on drugs,” but it has resulted in the deaths of many drug users.
Sadly, efforts to help those struggling with addiction are underfunded and disorganized, making it difficult for them to get the support they need.
Government initiatives to improve the Philippine healthcare system
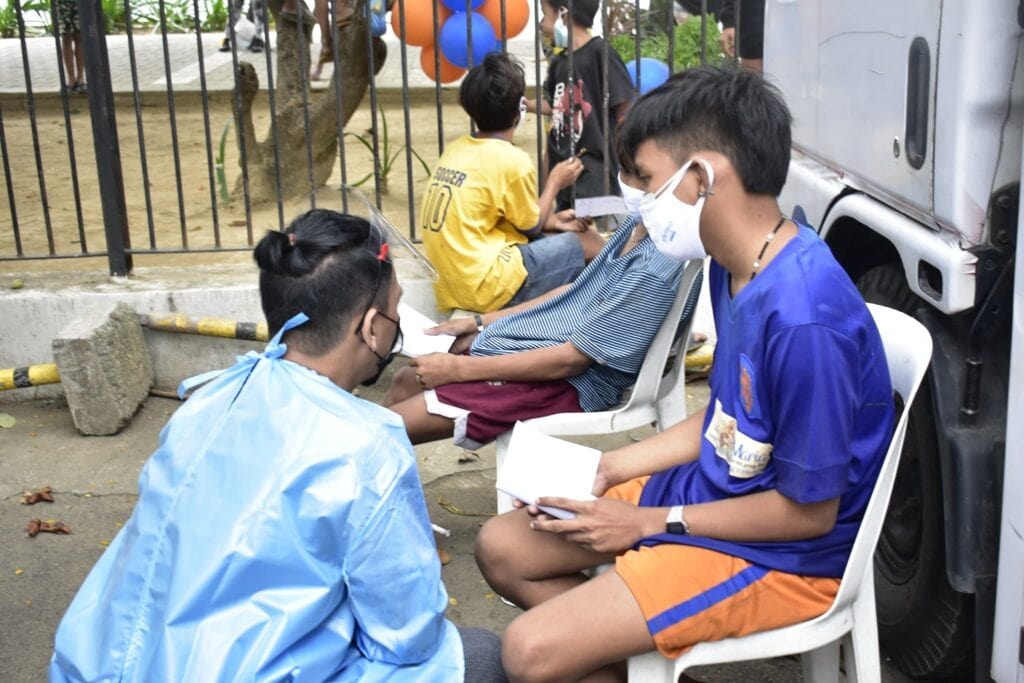

The Philippine government is working hard to make sure everyone in the country has access to good healthcare. They have taken on several initiatives to make this happen, including:
1. Increasing funding for the healthcare sector
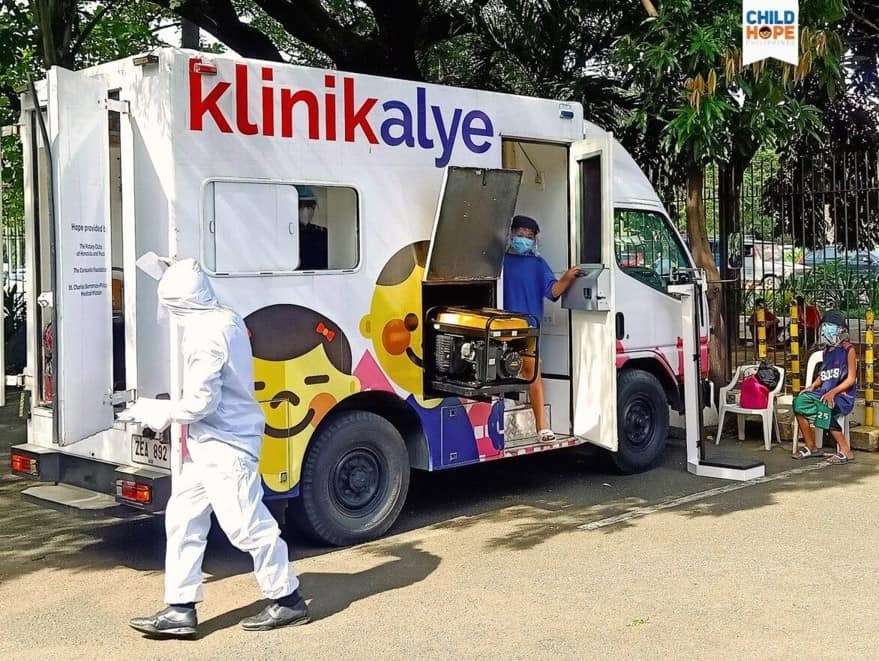

The government has increased the amount of money they spend on healthcare. This has helped to make public hospitals and clinics better.
They have bought new medical equipment, hired more healthcare workers, and made the places where patients get treated better.
The government has also started new public health programs focusing on specific health problems in the Philippines, like malnutrition and diseases that can spread from person to person.
One of these programs is the PhilHealth benefit package expansion. It ensures that all Filipinos have health insurance coverage and more medical procedures, like dialysis and cancer treatment.
The Health Facilities Enhancement Program is another initiative. It aims to make public health facilities better all over the country.
This includes building new rural health units and fixing up the old ones. This has made it easier for people who live in rural areas to get good healthcare.
2. Implementing health insurance programs
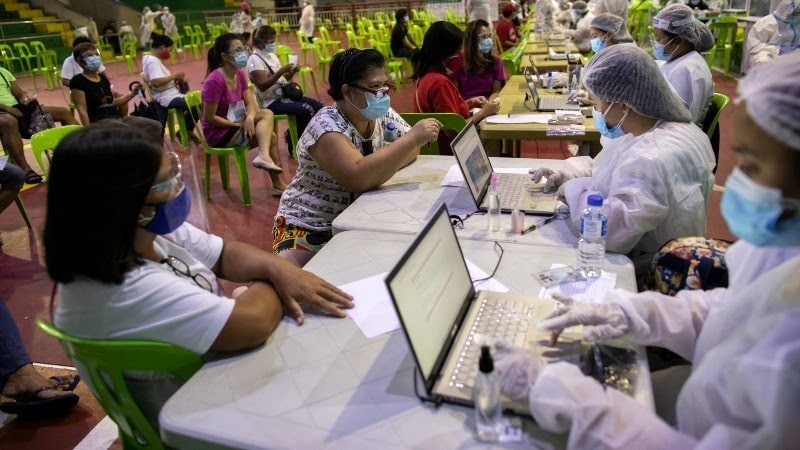

The Philippine government has started several health insurance programs to ensure that everyone can get healthcare services and that they are not too expensive. The PhilHealth program is the most well-known.
It gives all Filipinos health insurance and covers many different healthcare services, like going to the hospital, having medical procedures, and getting preventive care.
Another initiative is the Universal Health Care (UHC) Law. This makes sure that everyone in the Philippines can get quality healthcare services.
The UHC Law makes PhilHealth coverage available to all Filipinos and requires employers to give health insurance to their workers.
The government also has programs to help people who can’t afford healthcare services. They make sure that no one is left behind.
3. Improving healthcare infrastructure
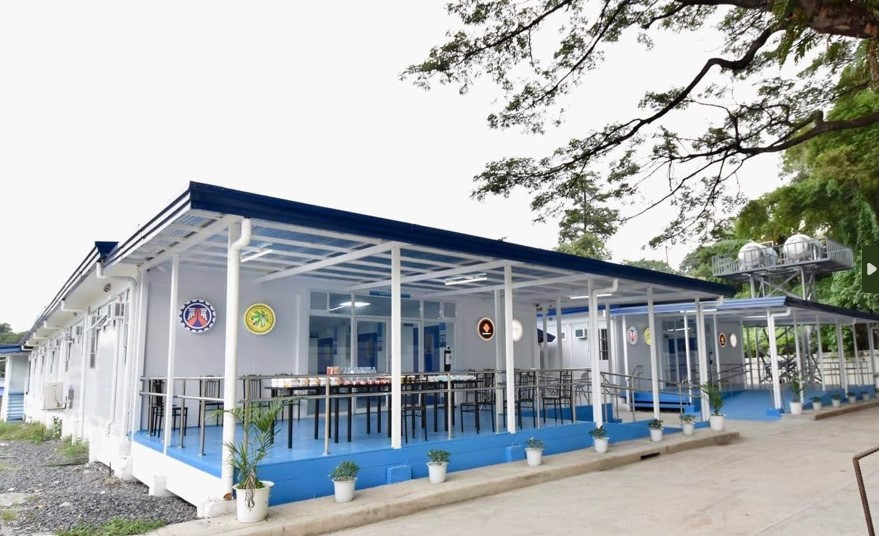

The Philippine government is also improving the healthcare system by improving the infrastructure. They are building new rural health units and fixing up the old ones.
These units give essential healthcare services to communities in remote and underserved areas. They provide services like prenatal care, immunization, and diagnostic tests.
The government is also upgrading public hospitals and clinics by providing them with modern medical equipment, making sure the places are clean and well-ventilated and hiring more healthcare workers.
They are doing this through partnerships with non-government organizations and international aid programs.
FAQs about the Philippine healthcare system
The Philippine healthcare system has come a long way, but more work still needs to be done. The government is focused on ensuring everyone has access to quality healthcare, regardless of their socio-economic status.
What has your experience of Philippine healthcare been like? Let us know in the comments!





